What I Built
In today's fast-paced business environment, managing calendar events across an organization can quickly become a nightmare. What starts as a simple request—"Can you create these recurring meetings for our team?"—often spirals into hours of manual calendar entry, especially when dealing with multiple attendees, group memberships, and changing schedules.
Solution Overview
This article walks through a complete PowerShell automation solution that transforms this tedious process into a set-and-forget system. The script automatically reads event definitions from an Excel file stored in SharePoint, sanitizes outdated entries, and leverages Microsoft Graph API (with Exchange Online fallback when needed) to create calendar events for individuals or entire groups within your organization.
Production-Ready Architecture
What sets this solution apart is its production-ready architecture: designed to run seamlessly both locally during development and in Azure Automation for hands-off operation, complete with robust logging, intelligent retry logic, and secure certificate-based authentication.
Tech Stack
Core Technologies
- PowerShell 5.1+
- Microsoft Graph PowerShell SDK
- Exchange Online PowerShell V3
- ImportExcel PowerShell Module
Infrastructure
- Azure Automation
- Certificate-based authentication
- SharePoint Online integration
Project Goals
How It Works
Challenges I Faced
Mixed Authentication Requirements
Microsoft Graph API doesn't support all Exchange operations yet, particularly distribution list management. I needed to maintain parallel authentication for both Graph API and Exchange Online PowerShell, with automatic token renewal for long-running processes.
SharePoint Path Resolution Complexities
SharePoint URLs can be tricky—"Shared Documents" in the UI becomes "Documents" in the API, spaces become "%20" in URLs, and nested folders require careful path construction. I implemented comprehensive path normalization logic to handle these common gotchas.
Group Type Detection and Member Expansion
Organizations use various group types: distribution lists (Exchange), Microsoft 365 groups (Azure AD), and security groups. Each requires different PowerShell commands to retrieve members. My solution implements a fallback strategy that tries multiple group resolution methods.
1. Global Configuration: The Foundation
Before diving into the code, let's understand the configuration strategy that makes this script both flexible and maintainable. Rather than hardcoding values throughout the script, all critical settings are centralized at the top.
Tenant and Application Settings
$TenantId = "your-tenant-id"
$TenantDomain = "yourcompany.onmicrosoft.com"
$ClientId = "your-app-registration-id"
$CertificateThumbprint = "your-certificate-thumbprint"In production Azure Automation, these values are pulled from Automation Account assets—encrypted variables that keep sensitive information secure while remaining accessible to your runbooks.
SharePoint Integration Points
$SiteURL = "https://yourcompany.sharepoint.com/sites/YourSite"
$LibraryName = "Shared Documents"
$ExcelFileName = "CalendarEvents.xlsx"2. Centralized Logging: Write-Log Function
Effective logging transforms debugging from guesswork into systematic analysis. The Write-Log helper function demonstrates how to build logging that adapts to its environment.
function Write-Log {
param(
[string]$Message,
[string]$Level = "INFO"
)
$Timestamp = Get-Date -Format "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
$LogMessage = "[$Timestamp] [$Level] $Message"
if ($IsRunningInAutomation) {
switch ($Level) {
"ERROR" { Write-Error $LogMessage }
"WARNING" { Write-Warning $LogMessage }
default { Write-Information $LogMessage -InformationAction Continue }
}
} else {
# Local execution with color coding
$Color = switch ($Level) {
"ERROR" { "Red" }
"WARNING" { "Yellow" }
"SUCCESS" { "Green" }
default { "White" }
}
Write-Host $LogMessage -ForegroundColor $Color
}
}3. Resilient API Calls: Invoke-WithRetry
Network calls to Microsoft Graph or Exchange Online can fail for numerous reasons: temporary connectivity issues, service throttling, or transient authentication problems. The Invoke-WithRetry function wraps these calls in intelligent retry logic.
function Invoke-WithRetry {
param(
[scriptblock]$ScriptBlock,
[int]$MaxRetries = $global:MaxRetryCount,
[int]$DelaySeconds = $global:RetryDelay
)
for ($i = 1; $i -le $MaxRetries; $i++) {
try {
return & $ScriptBlock
}
catch {
Write-Log "Attempt $i failed: $($_.Exception.Message)" "WARNING"
if ($i -eq $MaxRetries) {
Write-Log "All $MaxRetries attempts failed" "ERROR"
throw
}
Start-Sleep -Seconds ($DelaySeconds * $i) # Exponential backoff
}
}
}Why Exponential Backoff?
The exponential backoff pattern prevents your script from overwhelming a struggling service. If the first retry waits 2 seconds, the second waits 4 seconds, and the third waits 6 seconds.
Key Features
Production-Ready
Designed for Azure Automation with comprehensive error handling
Certificate Authentication
Secure, unattended authentication without storing passwords
Intelligent Retry Logic
Handles API throttling and temporary failures gracefully
Mixed Group Support
Works with both distribution lists and M365 groups
Duplicate Prevention
Smart detection prevents redundant calendar entries
Comprehensive Logging
Detailed logs for troubleshooting and audit trails
Data Validation
Thorough input validation prevents partial failures
Automatic Cleanup
Removes outdated event definitions automatically
Full Code Repository
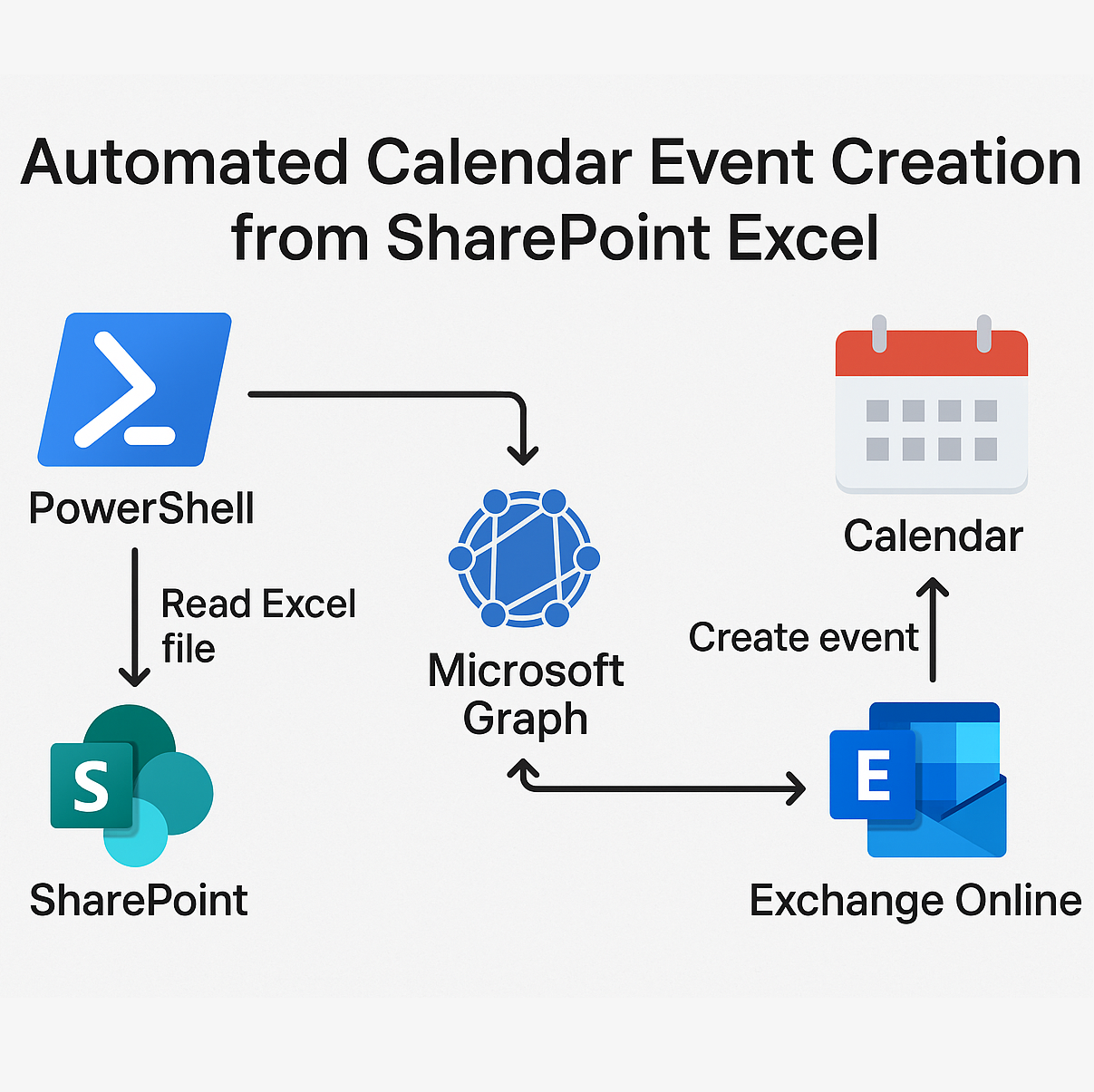
Calendar Automation Architecture
You can find the complete PowerShell script with all functions and error handling in my GitHub repository. The script includes detailed comments and can be easily customized for your organization's needs.
View Complete Script on GitHubReal-World Impact
This automation solution has transformed how organizations handle calendar management:
Time Savings
Reduces manual calendar entry from hours to minutes
Accuracy
Eliminates human errors in event creation and group expansion
Scalability
Handles hundreds of attendees across multiple groups effortlessly
Consistency
Ensures standardized event formatting and organizer assignment
Maintainability
Business users can update event definitions without IT involvement
Wrap-Up
This calendar automation script demonstrates several patterns that extend far beyond calendar management: robust configuration management, resilient API integration, comprehensive validation, and environment-aware logging. Whether you're managing calendars, processing data, or orchestrating complex workflows, these principles provide a template for building reliable automation that business users can depend on.
The combination of PowerShell's flexibility, Microsoft Graph's capabilities, and Azure Automation's reliability creates a powerful platform for business process automation. I hope this deep dive helps you build better automation solutions for your organization!
