The Challenge
Do you have important Intune remediations scripts running daily or weekly? What if you could get a detailed report on devices that failed to run or have a "With Issues" status automatically without having to go to the Intune Management portal and checking the remediations manually?
This is what brought me to build a solution that will do just that, and even more.
Solution Overview
An automated alerting system that monitors Intune remediation scripts and sends detailed reports via Teams notifications and email alerts using Azure Automation Account with managed identity.
Prerequisites
Azure Requirements
- Azure Automation Account with System Assigned Managed-Identity enabled
- Account with at least Cloud Application Admin permissions
PowerShell Modules
-
Microsoft.Graph -
Microsoft.Graph.Applications
Setting Up Permissions
To assign permissions to the managed-identity of our Automation Account, run the PowerShell script below. First, a few important notes:
⚠️ Configuration Notes
- • Fill in your tenant ID and the Enterprise Application name created when you enabled the System assigned Managed-Identity
- • Find the Enterprise Application by searching the Object (principal) ID from the Automation account's Identity section in Entra ID
- • The Microsoft Graph App ID (
$graphAppId) is the same for all tenants
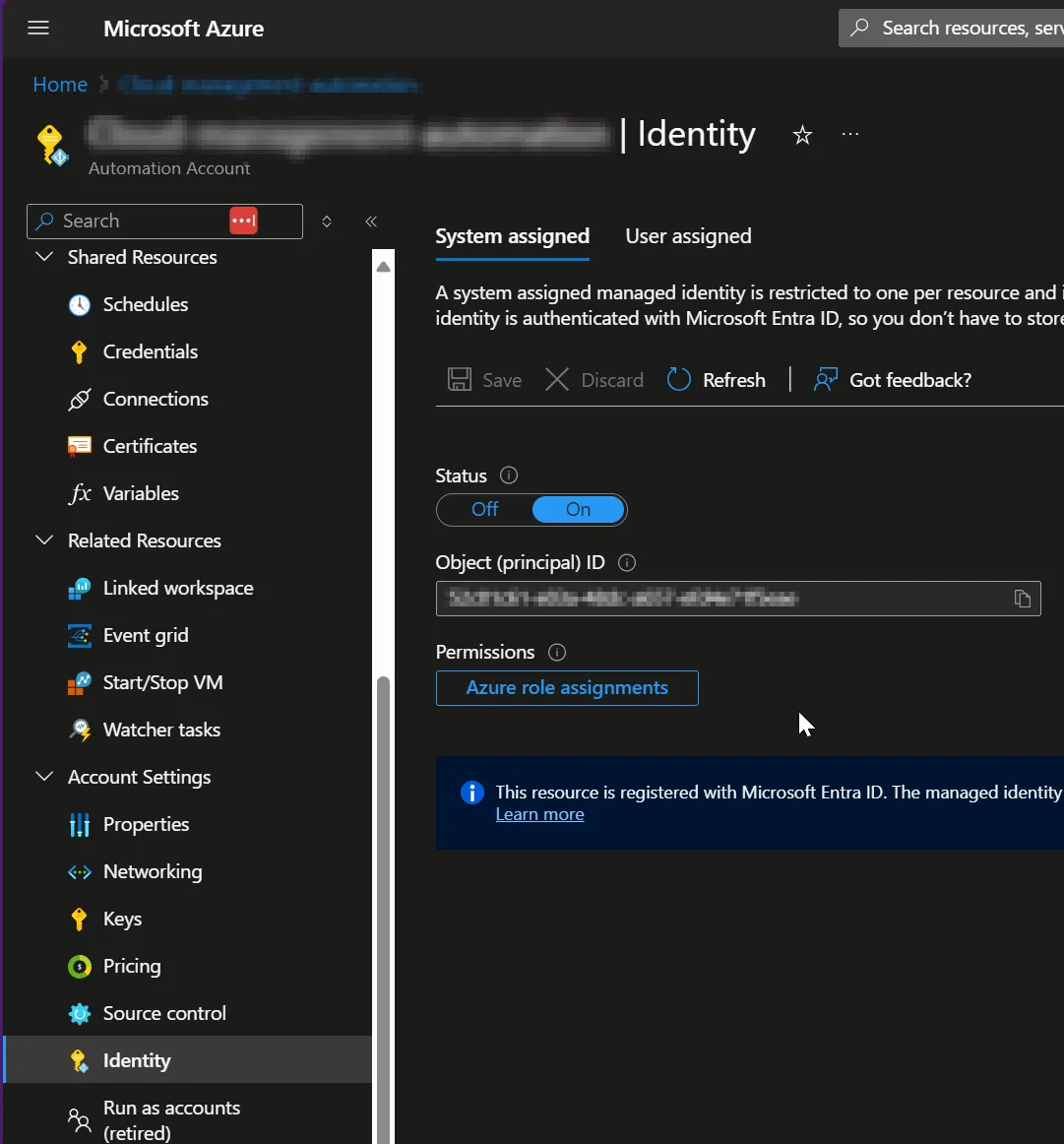
Automation Account Identity section showing Object (principal) ID
Permissions Assignment Script
This script assigns the required Microsoft Graph permissions to your Automation Account managed-identity. See the permissions documentation for more details.
$tenantID = "123456-1234-5678-1234-12345678"
$graphAppId = "00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000"
$permissions = @("Device.Read.All", "DeviceManagementManagedDevices.Read.All", "DeviceManagementConfiguration.Read.All")
$managedIdentities = @("EnterpriseApplicationName")
Connect-MgGraph -TenantId $tenantID -Scopes "AppRoleAssignment.ReadWrite.All", "Directory.Read.All"
$sp = Get-MgServicePrincipal -Filter "appId eq '$graphAppId'"
$managedIdentities | ForEach-Object {
$msi = Get-MgServicePrincipal -Filter "displayName eq '$_'"
$appRoles = $sp.AppRoles | Where-Object {($_.Value -in $permissions) -and ($_.AllowedMemberTypes -contains "Application")}
$appRoles | ForEach-Object {
$appRoleAssignment = @{
"PrincipalId" = $msi.Id
"ResourceId" = $sp.Id
"AppRoleId" = $_.Id
}
New-MgServicePrincipalAppRoleAssignment -ServicePrincipalId $appRoleAssignment.PrincipalId -BodyParameter $appRoleAssignment -Verbose
}
}
Disconnect-MgGraphGetting Remediation Script ID
Now that we have the permissions assigned, we can get the details needed for our Runbook. There are 2 ways to get the remediation script ID from Intune:
Option 1: Graph Explorer
Use Microsoft Graph Explorer to query remediation scripts
Option 2: Browser Dev Tools (Easier)
Use F12 developer tools in the Intune portal
Using Browser Developer Tools
- 1 Navigate to the Remediation script policy page in Intune portal
- 2 Press F12 to open the browser's Developer Tools
- 3 Switch to the Network tab, refresh the page
- 4 Scroll down to find the "runSummary" call and extract the remediation ID from the URL
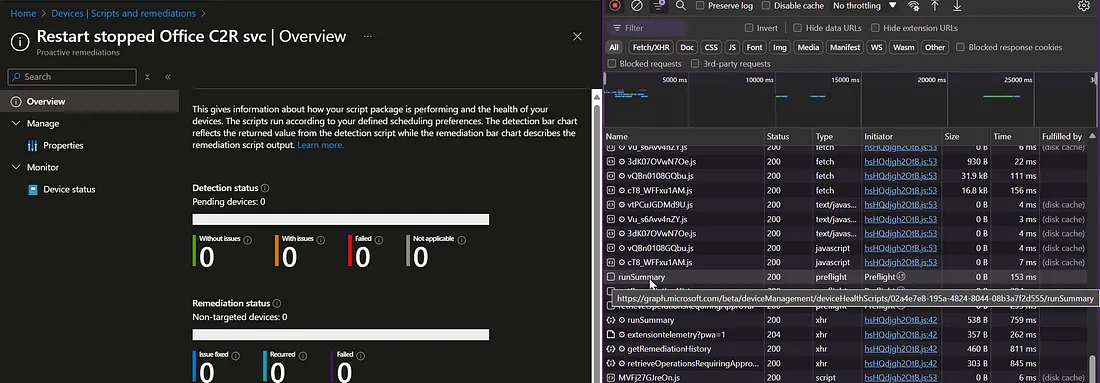
F12 Developer Tools Network tab showing remediation script calls
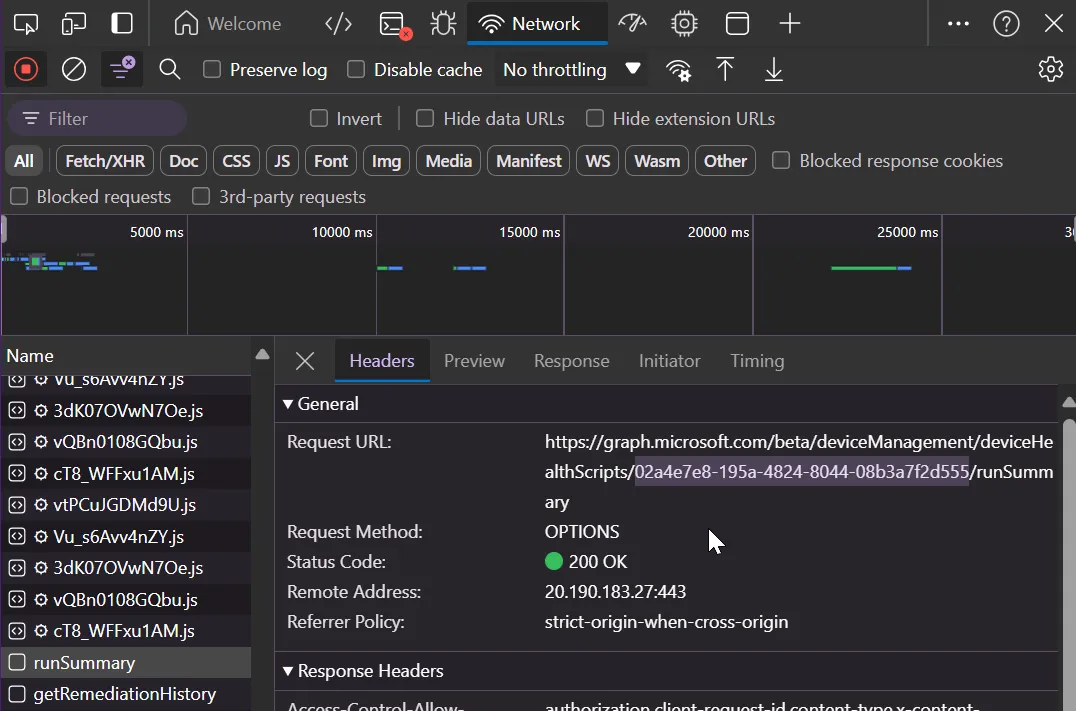
Click on the runSummary call to see the request URL and copy the remediation script ID
Automation Runbook Setup
Now we can create a Runbook on our Automation Account and paste the code from my script hosted on GitHub: Intune-RemediationScripts-Alerts.ps1
Teams Integration
To configure the Teams webhook needed for notifications, read the Microsoft documentation here.
After setting the webhook, configure the script variables:
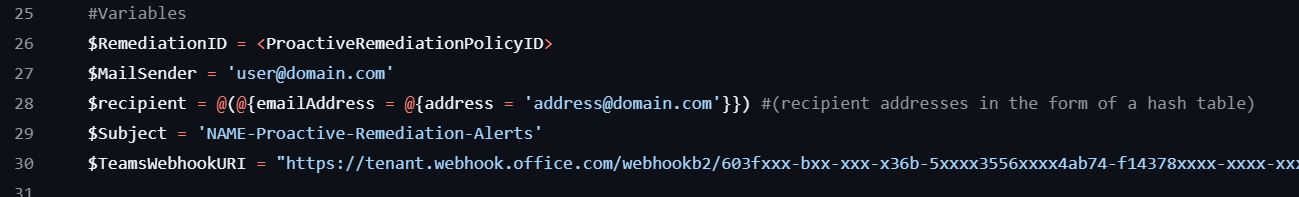
Variables section - configure your specific settings here
Note: Line 121 is where the notification is sent to a Teams channel. You can comment that line if you don't want to get a Teams notification.
Email Integration (Optional)
If you wish to send email using Exchange Online, you can grant permissions for your Managed-Identity with this script:
Connect-MgGraph -Scopes AppRoleAssignment.ReadWrite.All,Application.Read.All
$AppRoleID = "dc50a0fb-09a3-484d-be87-e023b12c6440"
$ResourceID = (Get-MgServicePrincipal -Filter "AppId eq '00000002-0000-0ff1-ce00-000000000000'").Id
$managedIdentities = @("EnterpriseApplicationName")
$msi = Get-MgServicePrincipal -Filter "displayName eq $managedIdentities"
New-MgServicePrincipalAppRoleAssignment -ServicePrincipalId $msi.Id -PrincipalId $msi.Id -AppRoleId $AppRoleID -ResourceId $ResourceIDRecommended SMTP Approach
I recommend using an SMTP service like Azure Email Communication Service to send emails as it requires fewer permissions.
Implementation Complete
I will update here or in another post about the configuration needed for uploading the data to a Log Analytics Workspace.
Schedule Your Automation
This is where this guide ends. You can now run your Runbook on a schedule to receive daily or weekly updates on your Intune Remediations scripts policies automatically!
